Testing Linux App Locally Using Epic’s Signaling Server
Before uploading your Linux-packaged Unreal app to the Eagle 3D Streaming platform, it's important to verify that it runs smoothly in a Pixel Streaming environment. This guide will walk you through testing your app locally using Epic’s Pixel Streaming Signaling Server.
Important Note
All steps must be performed on a Linux machine.
Ensure your Unreal project has the Pixel Streaming plugin enabled.
The app should already be packaged for Linux.
Follow the steps below:
Step 1. Run the .sh file as Desktop App
Run the packaged .sh file directly:
chmod +x YourProjectName.sh
./YourProjectName.sh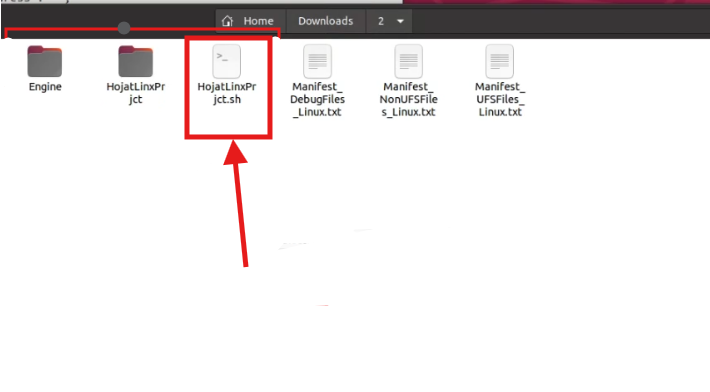
Figure 1. Run the .sh File
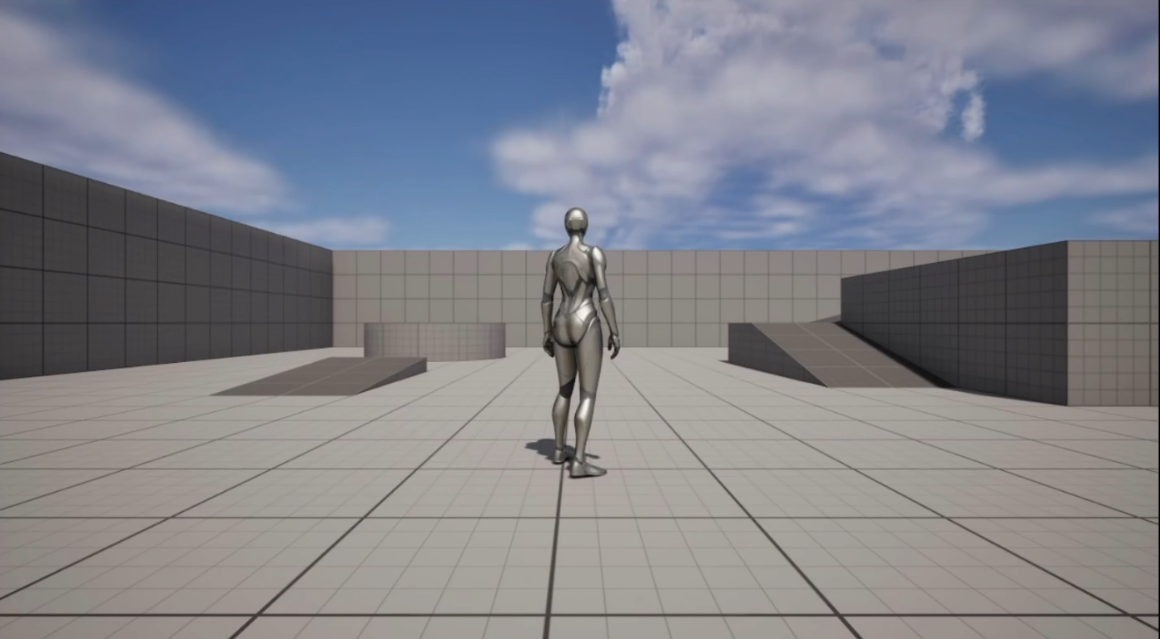

Figure 2. App is Running
If the application does not launch as a standard desktop app, the packaged build is invalid. In that case, it will not work with Pixel Streaming.
Step 2. Navigate to the WebServers Folder
Navigate To: [Your App Folder] → Samples → PixelStreaming → WebServers
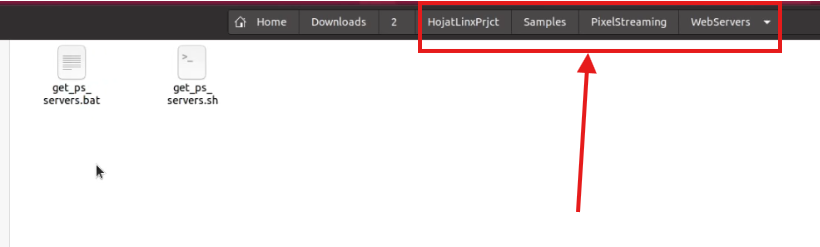
Figure 3. Navigate to WebServers Folder
Step 3. Open Terminal in the WebServers Directory
Step 4. Make the Script Executable
Run the following command:
chmod a+x get_ps_servers.sh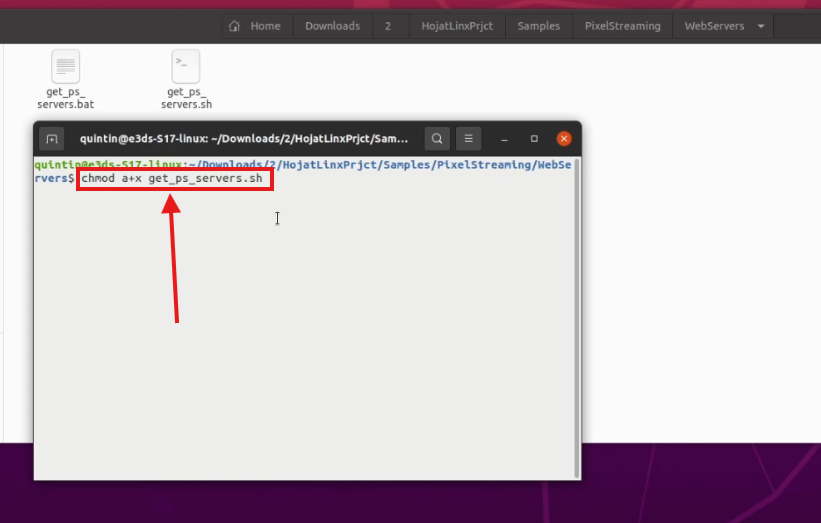
Figure 4. Running chmod
Step 5. Run the shell command :
./get_ps_servers.shIf you see an error like “No such file or directory,” proceed to Step 5. Else go to Step 10.
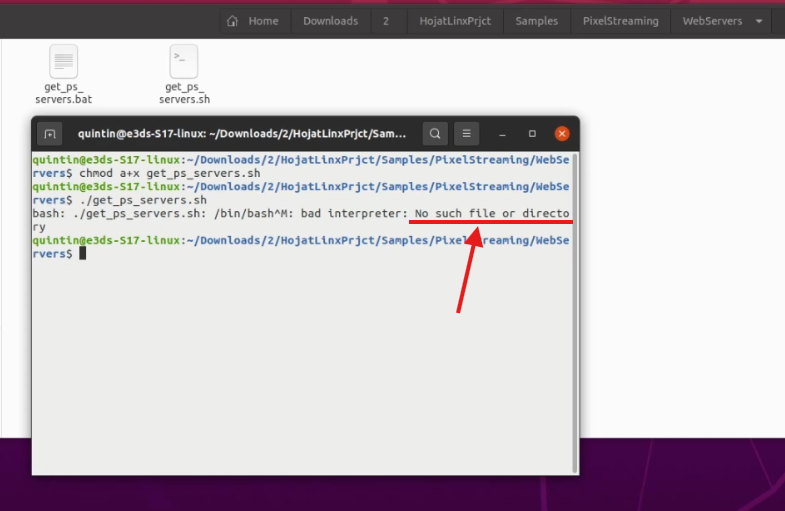
Figure 5. No Such Directory
Step 6. Check if curl is Installed
Run:
which curl 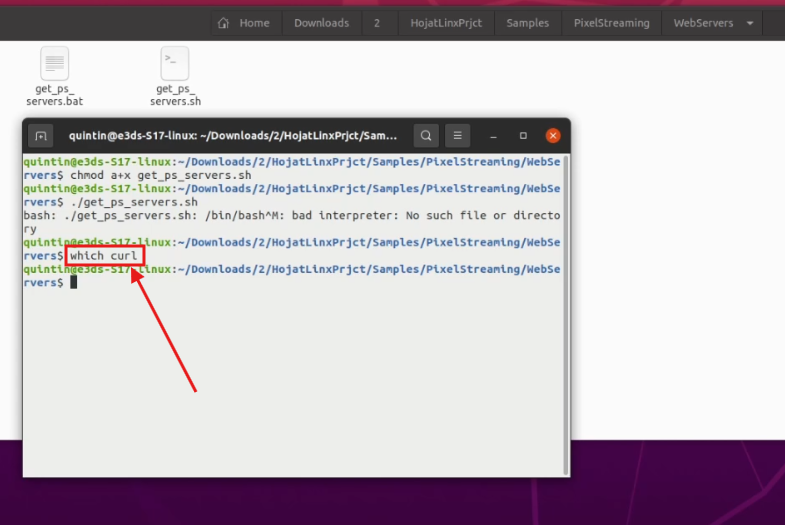
Figure 6. Checking curl
If there’s no output, install curl in the next step.
Step 7. Install curl
Run:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall curl You may be prompted for your password.
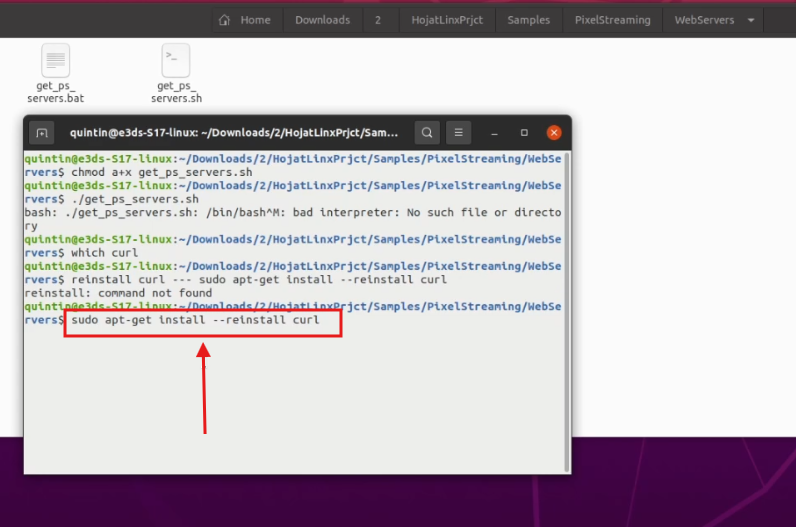
Figure 7. Installing curl
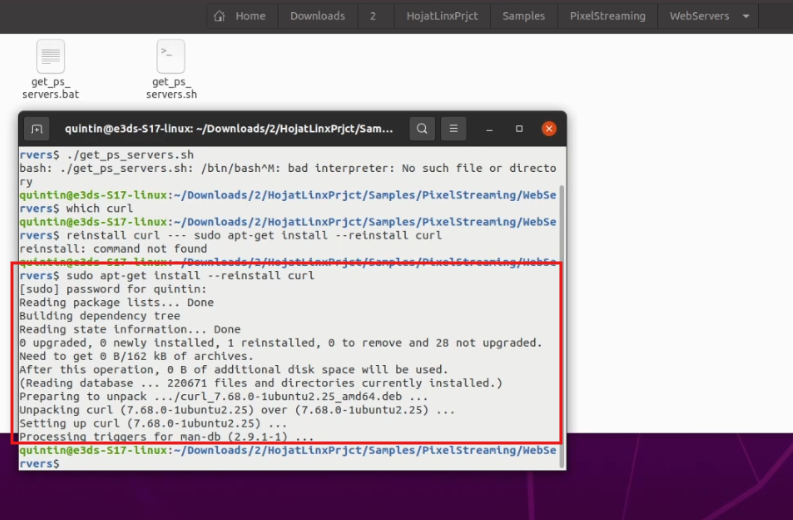
Figure 8. curl Installed
Step 8. Retry the command
Re-run the following:
chmod a+x get_ps_servers.sh./get_ps_servers.shIf it still fails, proceed to Step 8.
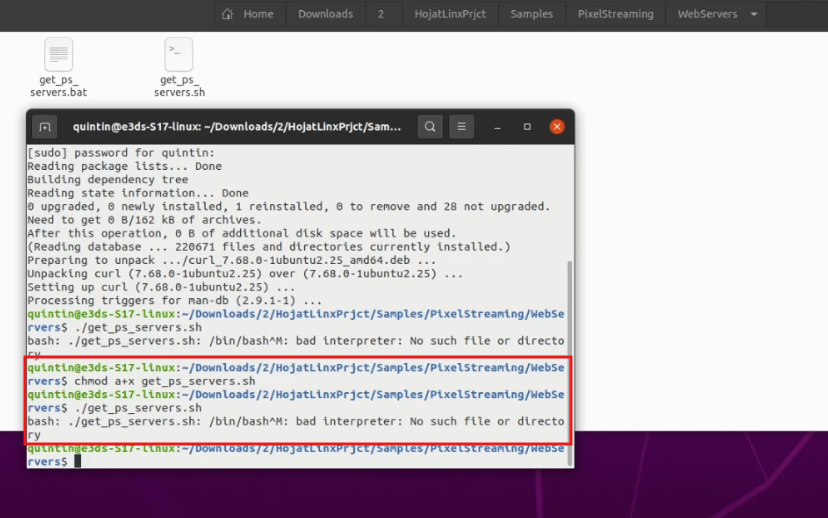
Figure 9. No Such File or Directory
Step 9. Convert command to UNIX Format
Run:
dos2unix get_ps_servers.sh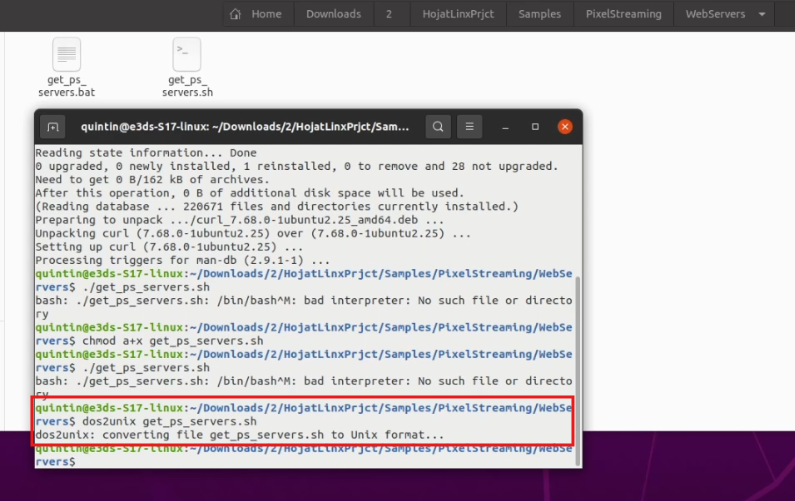
Figure 10. Converting to UNIX Format
Step 10. Run the command Again
chmod a+x get_ps_servers.sh./get_ps_servers.shYou should now see folders like SignalingWebServer, SFU, etc.
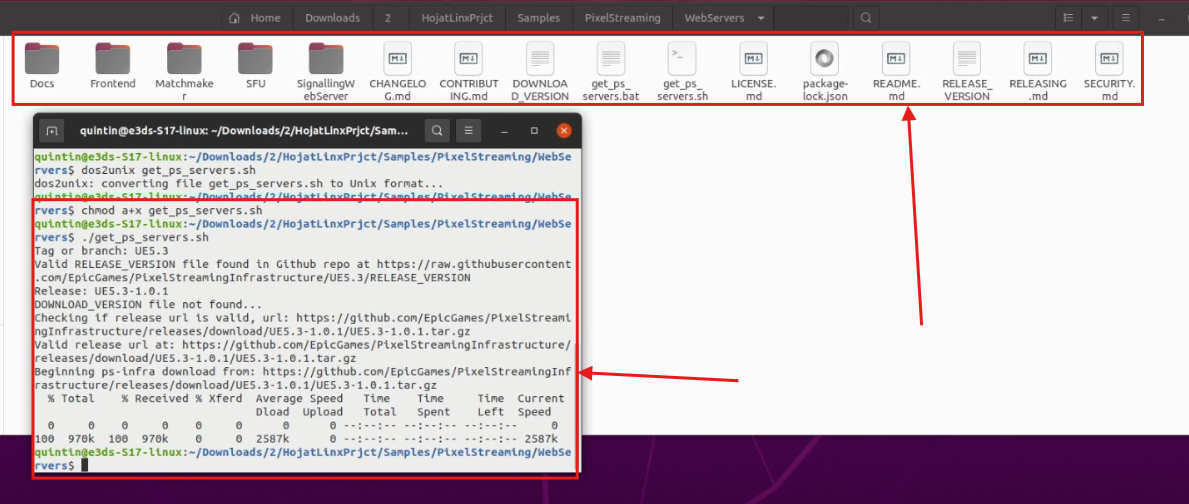
Figure 11. Some Files & Folders are Downloaded
Step 11. Navigate to bash folder
Go to:
SignalingWebServer → platform_scripts → bash
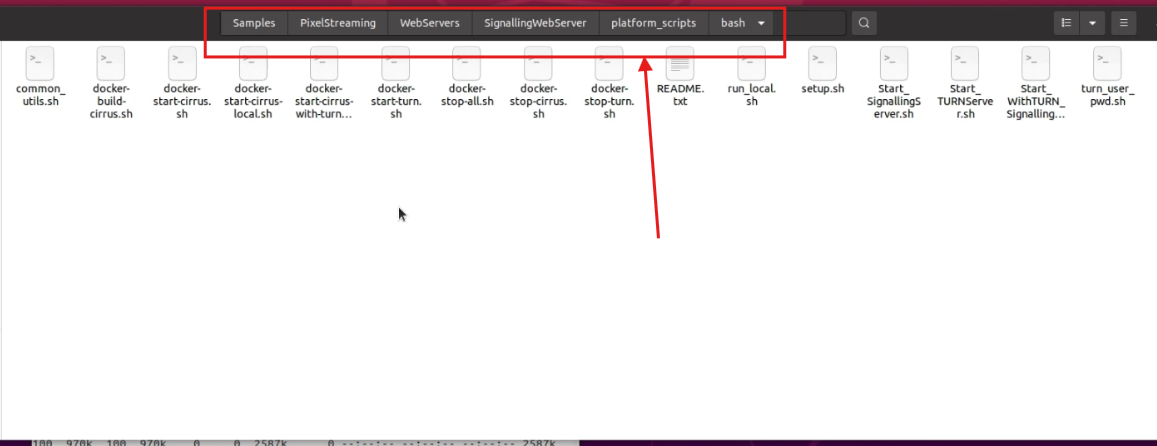
Figure 12. Navigate to bash Folder
Start 12. Open Terminal in Bash Folder
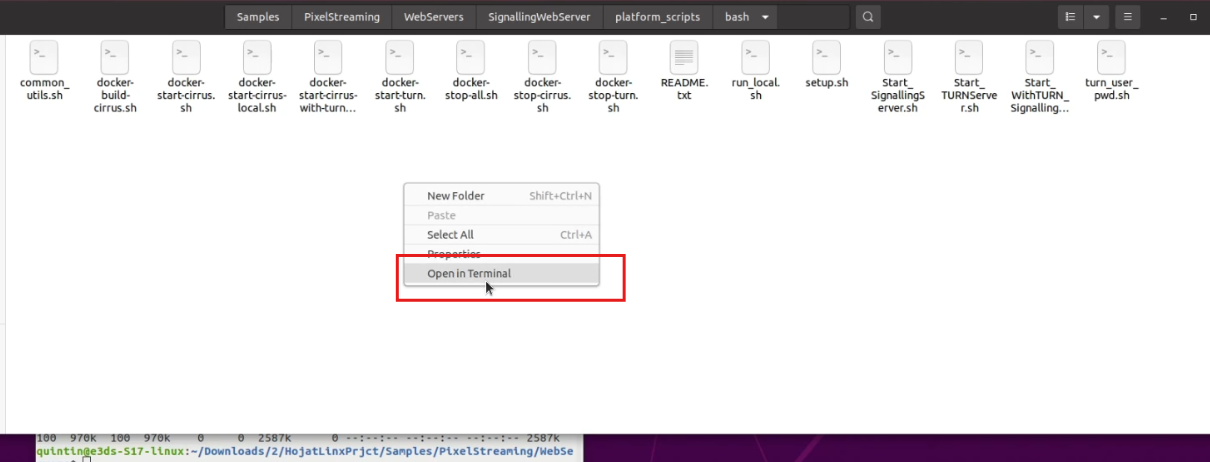
Figure 13. Open in Terminal
Step 13. Start the Signaling Server
In the terminal, run:
./run_local.shYou may be prompted for your password again.
Leave this terminal window open. Do not close it while testing your app.
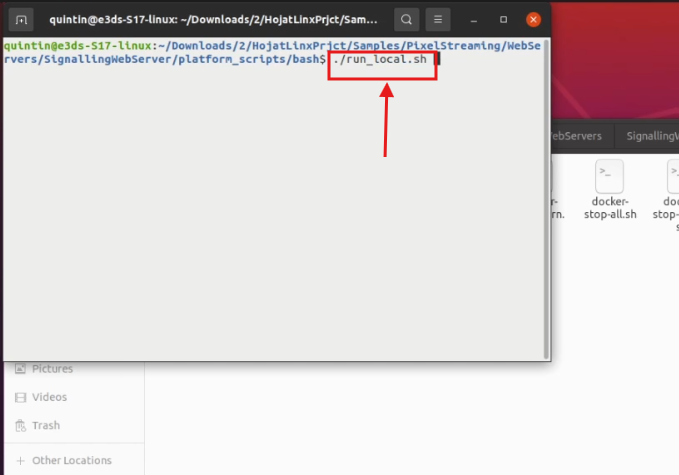
Figure 14. Start the Signaling Server
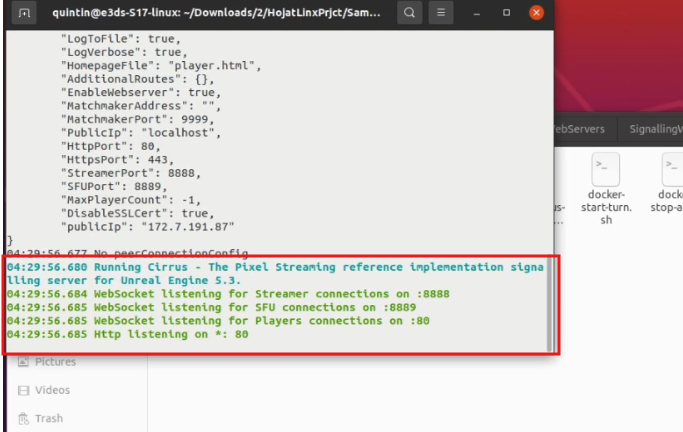
Figure 15. Signaling Server Running
Step 14. Open App Root Folder in Terminal
Root folder is the folder containing your Engine folder and .sh app script.
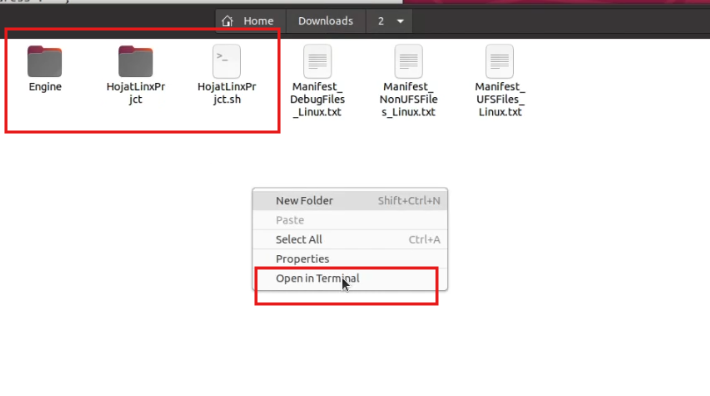
Figure 16. Open Root Folder in a Terminal
Step 15. Create a new .sh file
Create a new file using the command below. (Use any name you want. Here we used HojatLinxPrjct2.sh)
Run:
vim GiveNewFileName.sh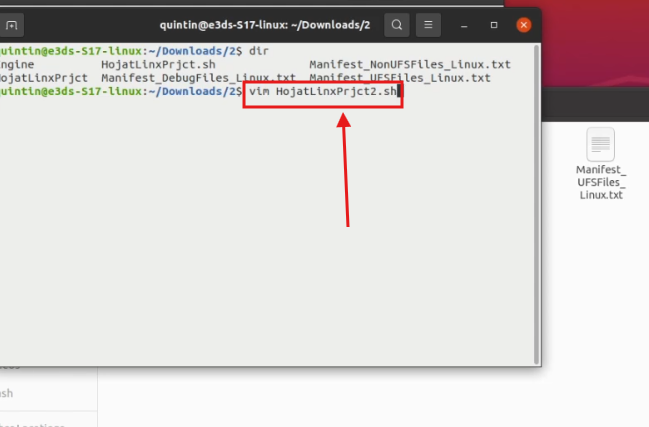
Figure 17. Create a New .sh File
A new blank file will open in the terminal where you can paste the script.
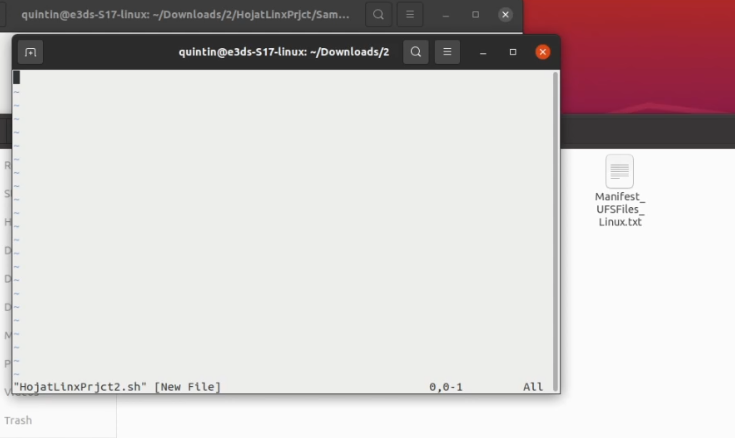
Figure 18. Created New File
Step 16. Build the script
Below is the script. You’ll need to modify the red-highlighted paths to match your actual app folder structure:
#!/bin/sh
UE_TRUE_SCRIPT_NAME=$(echo "$0" | xargs readlink -f)
UE_PROJECT_ROOT=$(dirname "$UE_TRUE_SCRIPT_NAME")
chmod +x "$UE_PROJECT_ROOT/HojatLinxPrjct/Binaries/Linux/HojatLinxPrjct"
"$UE_PROJECT_ROOT/HojatLinxPrjct/Binaries/Linux/HojatLinxPrjct" HojatLinxPrjct \
-log -AudioMixer -PixelStreamingIP=localhost -PixelStreamingPort=8888 -RenderOffScreen "$@"
In our case the file location is showing here
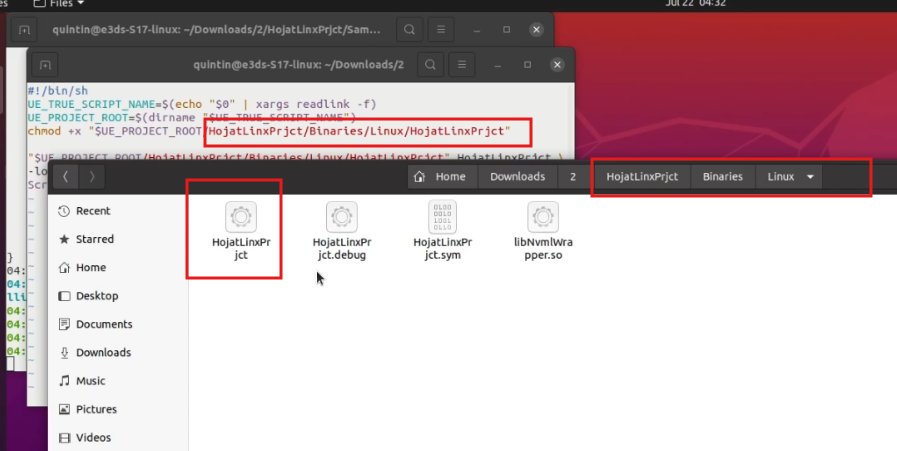
Figure 19. Create Script Based on Linux File Location
We’ve included the script again below so you can copy it easily.
#!/bin/sh
UE_TRUE_SCRIPT_NAME=$(echo "$0" | xargs readlink -f)
UE_PROJECT_ROOT=$(dirname "$UE_TRUE_SCRIPT_NAME")
chmod +x "$UE_PROJECT_ROOT/HojatLinxPrjct/Binaries/Linux/HojatLinxPrjct"
"$UE_PROJECT_ROOT/HojatLinxPrjct/Binaries/Linux/HojatLinxPrjct" HojatLinxPrjct \
-log -AudioMixer -PixelStreamingIP=localhost -PixelStreamingPort=8888 -RenderOffScreen "$@"Step 17. Pass the script in the terminal of new file that you have created on step 14
Add a warning not to press enter
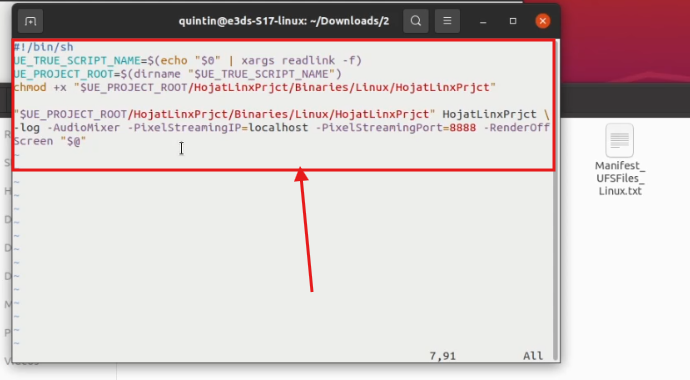
Figure 20. Passing the Script
Step 18. After pasting the script, press : then type wq and press Enter.
:wq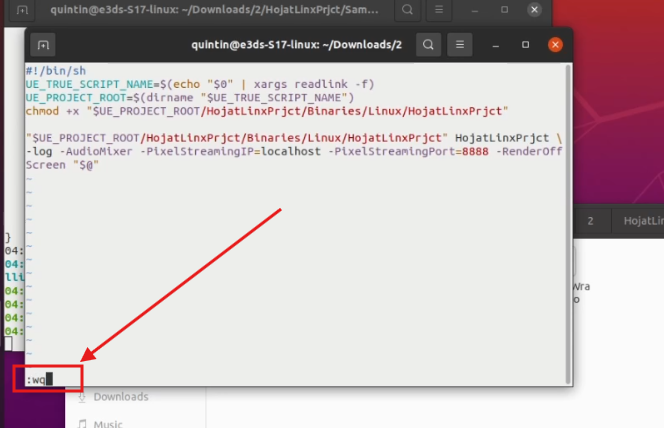
Figure 21. Type :wq and Press Enter Key
Step 19. Check newly created file
Run:
dir 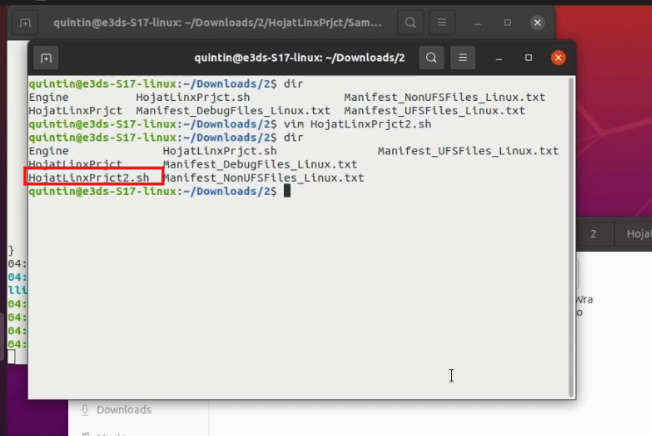
Figure 22. Newly Created File
Step 20. Make the Script Executable
Run:
chmod a+x YourNewlyCreatedFile.shYou should use your newly created file name instead of YourNewlyCreatedFile.sh.
In our case the newly created file name is HojatLinxPrjc2.sh. So we used this name
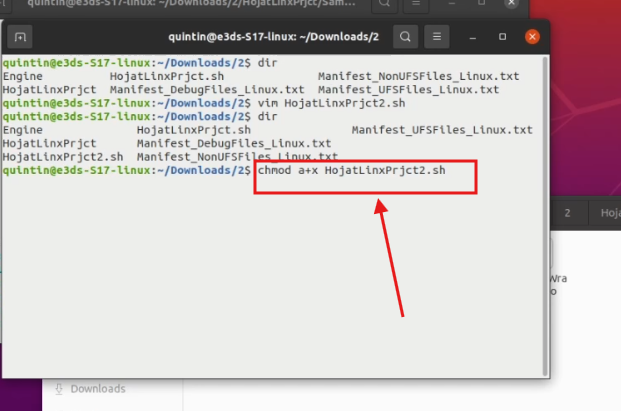
Figure 23. Make the Script Executable
Step 21. Start the App
Run:
./YourNewlyCreatedFile.sh.You should use your newly created file name instead of YourNewlyCreatedFile.sh.
In our case the newly created file name is HojatLinxPrjc2.sh. So we used this name.
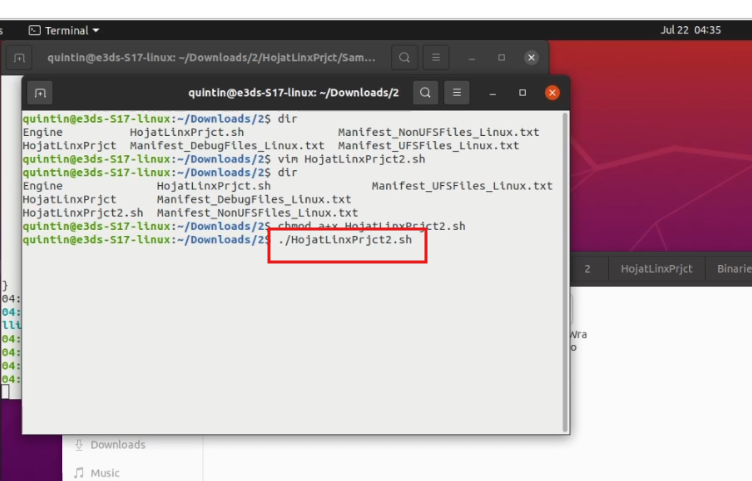
Figure 24. Run the App
You may need to give password. Give it.
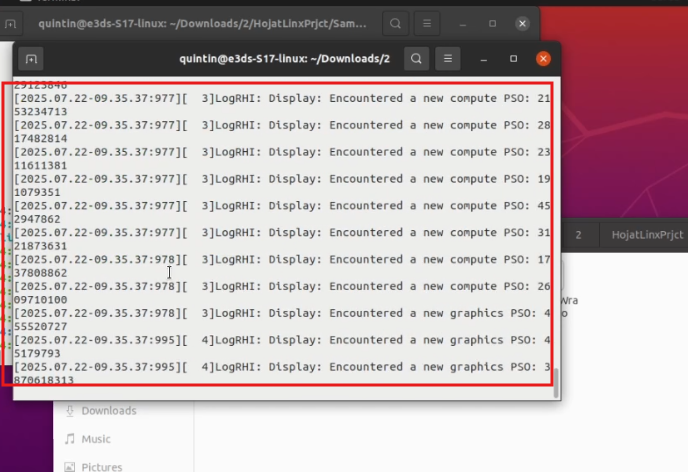
Figure 25. App is Started
Step 22. Launch the App in Browser
On the same Linux computer, go to your browser and visit:
localhost
Click on “CLICK TO START” to launch the app.
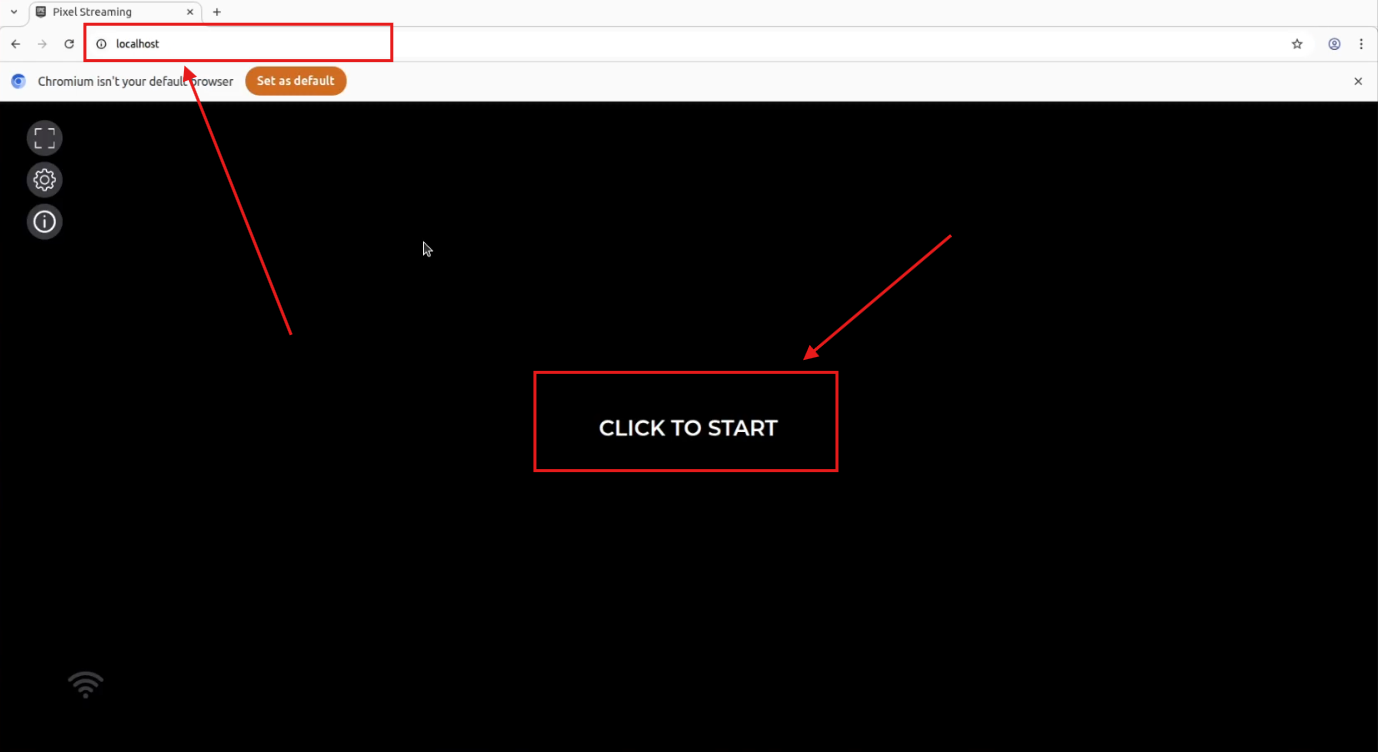
Figure 26. Click to Start
You should see your app streaming locally.
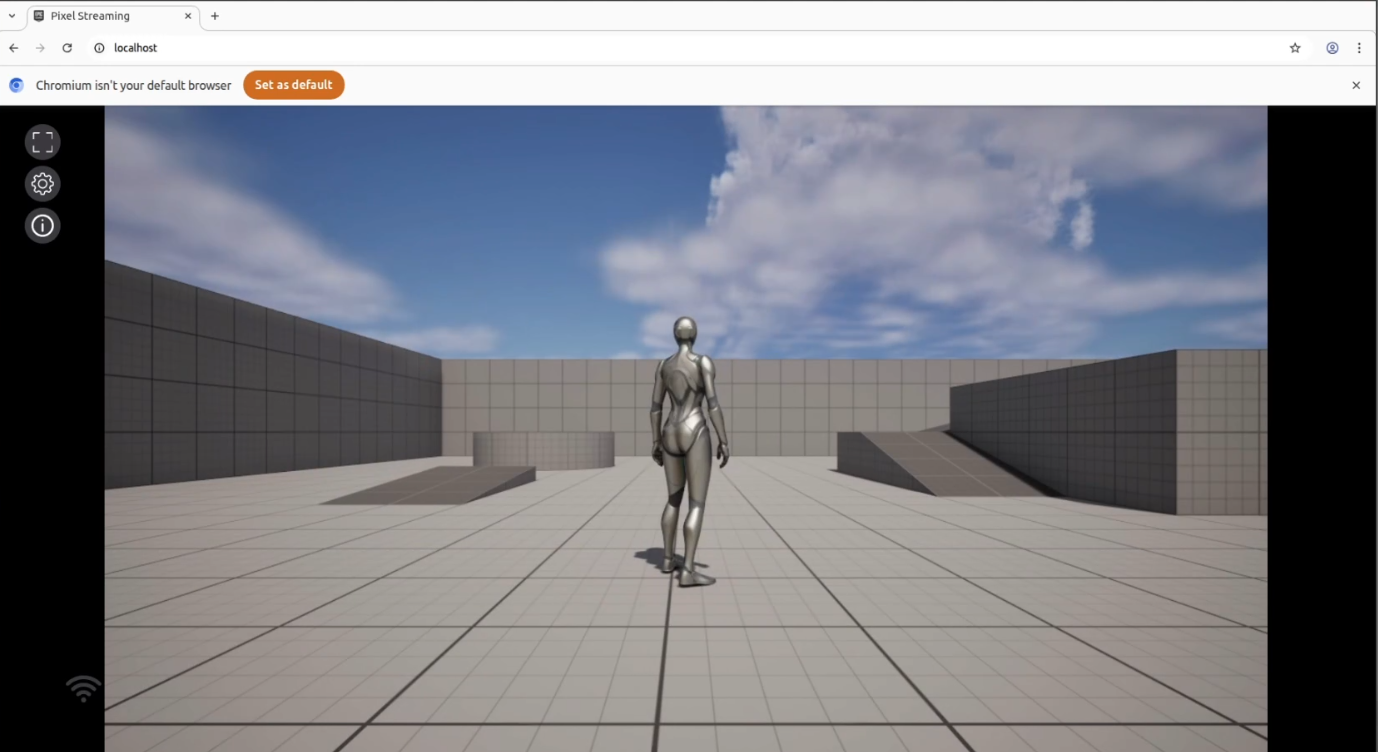
Figure 27. App is Running
🌐 Remote Testing Option
You can also test remotely under the same network by:
Getting the PC’s IP Address:
hostname -I Enter that IP in a browser from another device:
http://<your-ip-address>Note: For testing outside the network (different Wi-Fi), a static IP is required.
(A full remote setup guide is coming soon.)
Need help?
🛠️ Contact our Support Team
💬 Join the Community on Discord
Follow us on:
Facebook | GitHub | LinkedIn | YouTube
